FAQs
Laser Diode Module Comparison — Visible to SWIR
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
450
nm Laser (Blue): A visible blue wavelength
producing a sharp, high-contrast beam. Blue lasers are highly visible and
effective for projection and fluorescence excitation.
Typical
Applications: Laser projectors, stage lighting, fluorescence
excitation, biomedical instrumentation, industrial alignment, and material
processing.
520
nm Laser (Green): The most visible wavelength to
the human eye, appearing much brighter than red or blue at the same power.
Provides a sharp, round dot with excellent beam quality, ideal for outdoor and
long-distance visibility.
Typical
Applications: Surveying, construction alignment, laser
pointers, stage displays, and precision measurement systems.
635
nm Laser (Red–Orange): A bright visible red laser with
high eye sensitivity compared to 650 nm. Provides superior visibility under
strong ambient light.
Typical
Applications: Laser pointers, leveling tools, alignment
systems, medical aiming beams, and display devices.
650
nm Laser (Deep Red): A widely available and
cost-effective red wavelength. Slightly less visible than 635 nm but popular
due to diode affordability and durability.
Typical
Applications: Barcode scanners, laser pointers, industrial
alignment, consumer electronics (DVD/CD players).
780
nm Laser (Near-IR / Deep Red): On the edge
of visible and NIR spectrum, appears as a faint deep red glow. Economical and
compatible with many optical systems.
Typical
Applications: Optical storage (CD/DVD drives), spectroscopy,
medical diagnostics, and alignment where partial visibility is acceptable.
850
nm Laser (Near-IR): The most popular NIR wavelength.
Invisible to the eye but highly compatible with silicon-based detectors, making
it ideal for IR cameras and sensors.
Typical
Applications: Night vision illumination, eye tracking,
industrial sensing, biometric authentication, medical imaging devices.
940
nm Laser (Near-IR, Deep): Fully invisible to the human
eye. Provides reduced interference with visible-light imaging systems and
enhanced stealth operation.
Typical
Applications: Security and surveillance, 3D sensing, gesture
recognition, consumer electronics (smartphones, AR/VR), covert eye-safe
illumination.
Typical Applications: Wafer and material inspection, spectroscopy, industrial sensing, and biomedical imaging.
The laser modules are critical components for industrial/technical applications. They are mounted inside machine and could emit more precise laser beam, ideal for industrial applications. Therefore, Quarton's laser module is the preference if you need to customize the unique specifications or work for high quality.
All of our laser modules are designed to
accept only specified certain range amount of voltage in order to operate the
laser, the power output of the laser module will not emit beyond the power
within the specification due to excessive voltage. The Laser output power must
be stable especially in safety reason.
1. The laser modules will emit heat while
they are working, high working temperature is frequently the reason for laser
failure, more than that, it may cause the laser spot size or laser line width
will be larger. Operate the laser module at proper temperature range can extend
its lifetime, each laser module has its specified temperature range. Besides,
you could add a heatsink to laser module in order to heat radiation.
2. Some series of laser module housing is
an electrical positive surface, it is imperative that contact between the laser
module and the machine be avoided. This is to prevent damage from the machine
electrical leakage.
3. Please don't pull vigorously the electrical leads. The two leads are the positive (red) and negative (black), be used for operating power.
Fan angle is the angle spread of laser beam, it will affect the line length of laser line (such as line or crosshairs) at a particular distance. The fan angle is bigger, the laser line is longer at certain distance. Length of laser line is proportional to the distance from laser module to projection surface.

Our dot laser
modules have ellipse dot and circular dot to be select, and there are line or
crosshairs laser modules.
The glass lens
can be used on relatively high power of laser modules and it could endure the
more temperature changes. It also has higher light transmission and better
scratch resistance.
The plastic lens is an economic and durability proposal. It is lighter than glass and can be designed for customized request easily, it means compatible with many laser module. For indoor application, it works almost same as glass lens. However out of room temperature range, plastic lens will cause defocus a little and laser dot could be fuzzy.
According to FDA requirements:
POLICY: In keeping with this recognition of a hazard and the advice given, the Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) will object to any intentional exposure of the public to hazardous levels (1.e., greater than Class I levels) of laser or collateral radiation (light) from this type of equipment. Further, the CDRH will object to any instructions or promotion of Class II or IIIa demonstration laser products (projectors, scanners, shows, etc.) that do not adequately warn the user to prevent such exposure.
Class I audience exposure levels.
Only Class I levels of laser radiation have no known hazard and these are the only exposure levels that are considered safe for direct exposure of people. Exposure of the audience to levels in excess of the Class I limits is not to be promoted or encouraged in any way.
Class II warning:
CAUTION Laser Radiation (or Light)
Do Not Stare Into Beam
Class IIIa warning: DANGER Laser Radiation (or Light)
Avoid Direct Eye Exposure
These levels are hazardous to the eyes. No direct or reflected beams may be directed into audience areas or used to scan the audience in any way. A projector certified as Class II or IIIa cannot be used for audience scanning unless the projector is equipped with an adequate scanning safeguard which will prevent scanning above the Class I limits and adequate user instructions for achieving the Class I levels are provided.
Class IIIb hand-held lasers are too dangerous for use as pointers or amusement articles. Furthermore, promotion of Class IIIb or IEC Class 3B products for pointing or amusement violates FDA requirements and United States law. Manufacturers of such products may be required to repair, replace, or refund the purchase price of violative products distributed in the U.S. These products are also subject to detention and seizure by the U.S. Customs and Border Protection when imported.
Irresponsible use of more powerful laser pointers poses a significant risk of injury to the people exposed. Persons who misuse or irresponsibly use lasers are open to personal liability and prosecution.
Reference: https://www.fda.gov/radiation-emitting-products/laser-products-and-instruments/important-information-laser-pointer-manufacturers
Our most laser modules are continuous wave
(CW) and can't be modulated. Therefore, we had additionally designed the laser
modules with modulation function, you could review our TTL modulation laser
modules on various category.
TTL Operation Function Diagram:
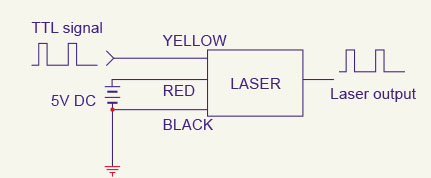
TTL Level:

Class IIIa or IEC Class 3R lasers can be dangerous. Class IIIa lasers can cause temporary visual effects such as flash blinding, which could distract or startle the person exposed. The risk of injury is very small when Class IIIa pointers are used responsibly because natural body motion of a person holding the pointer or motion of a person who might be exposed makes it difficult to expose the eyes for a long period of time. People also have a natural aversion to bright lights and are likely to close their eyes and turn their heads if exposed.




